Introduction
Choroidal excavation is a novel entity that is diagnosed with optical coherence tomography (OCT). In 1959, Klien, et al. [1] first described a concave-shaped chorioretinal abnormality with undifferentiated choriocapillaris and retinal pigment epithelium. Then in 2006, Jampol [2] defined similar changes with OCT and first used the term of focal choroidal excavation (FCE). In 2011, Margolis, et al. [3] described two FCE patterns, based on the shape of the lesions: nonconforming, if the photoreceptors are detached from retina pigment epithelium (RPE) and conforming, when the RPE follows the photoreceptor layer without any optically clear space between the outer retina and RPE. These two forms are also thought to convert to each other during the clinical process of the disease [4]. Although it is known to be mostly idiopathic, its relationship with central serous chorioretinopathy, choroidal neovascular membrane and inflammatory diseases such as multiple evanescent white dot syndrome and Vogt Koyanagi Harada disease has been reported [5]. In this report, we present a patient with multiple focal choroidal excavation following protein-rich diet.
Case
21-year-old male patient applied with blurred vision in his right eye since one week. He was on a protein rich diet since he was doing bodybuilding and had been using approximately 2g/kg/day protein powder since 3 months. His best corrected visual acuity was 0,6 in his right eye (RE) and 0,9 in his left eye (LE). There was no refractive disorder. Slit lamp examination and intraocular pressure were normal. Fundus examination revealed cavitary lesions in the macula of the RE (Figure 1a) and pigmentary changes above the macula of the LE (Figure 1b). OCT showed multiple conforming (Figure 2a) and non-conforming (Figure 2b) type of focal choroidal excavations with small retinal pigment epithelium detachments in the right eye and a small retinal pigment epithelium detachment in the left eye (Figure 2c). When evaluated with fundus autofluorescence (FAF), there have been hypo and hyperautofluorescent areas in the macula of the right eye in accordance with the pigmentary changes (Figure 3a) and hypoautofluorescent area above the macula of the left eye (Figure 3b). Fundus fluorescein angiography showed multiple hyperfluorescent window defects in the macula of the RE and hyperfluorecence consistent with window defect above macula of the LE. There was no ischemia, leakage, macular edema and all vascular structures were normal . Protein powder stopped and the patient was examined 6 months after the diagnosis. No changes in the findings were detected.
Read more about this article : https://lupinepublishers.com/ophthalmology-journal/fulltext/multiple-focal-choroidal-excavations-in-association-with-protein-rich-diet.ID.000158.php
Read More About Lupine Google Scholar: https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=en&user=T4c9RDkAAAAJ&citation_for_view=T4c9RDkAAAAJ:blknAaTinKkC
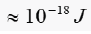 which is on the verge of thermal fluctuations
which is on the verge of thermal fluctuations  This means that a billion
(109) transistor chip uses order energy in a single act 10-3J. Then,
in order of speed 1GHz , the energy consumed can reach values
This means that a billion
(109) transistor chip uses order energy in a single act 10-3J. Then,
in order of speed 1GHz , the energy consumed can reach values 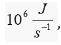 far exceeding the power of a jogging electric kettle
far exceeding the power of a jogging electric kettle 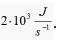
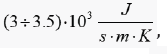 which significantly exceeds
the thermal conductivity of diamon
which significantly exceeds
the thermal conductivity of diamon 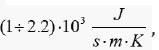 which was considered one of the best heat conductors. Carbon nanotubes
are
thermally stable, characterized by high electrical conductivity [10],
high electron mobility [11], and a large specific surface value [15]. It
is believed [16] that the abnormally high thermal conductivity
of carbon nanotubes is due to their regular structure and the small
number of defects and impurity centers in them. In the elementary
cell of graphene there are two carbon atoms, so the dispersion
spectrum consists of three optical and three acoustic branches,
among which the longitudinal and transverse acoustic modes
correspond to the speed of sound 2130 and 1360 M/s
which was considered one of the best heat conductors. Carbon nanotubes
are
thermally stable, characterized by high electrical conductivity [10],
high electron mobility [11], and a large specific surface value [15]. It
is believed [16] that the abnormally high thermal conductivity
of carbon nanotubes is due to their regular structure and the small
number of defects and impurity centers in them. In the elementary
cell of graphene there are two carbon atoms, so the dispersion
spectrum consists of three optical and three acoustic branches,
among which the longitudinal and transverse acoustic modes
correspond to the speed of sound 2130 and 1360 M/s